Difference between revisions of "Practice Identifying percentile ranks and scores based on standard deviation"
(Created page with "File:Normal.jpeg == Suppose a test on math anxiety was given to a large group of individuals and the scores are from a normally distributed population in which the mean...") |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| + | == Suppose a test on math anxiety was given to a large group of individuals and the scores are from a normally distributed population in which the mean is 50 and the SD is 10 == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Normal.jpg]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
1) Approximately what % of individuals earned scores below 50? | 1) Approximately what % of individuals earned scores below 50? | ||
Revision as of 12:16, 29 October 2019
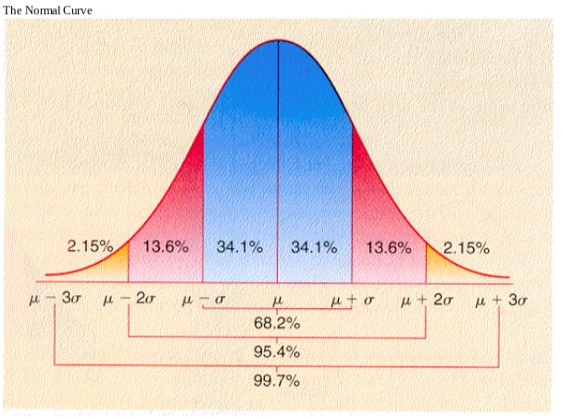
Suppose a test on math anxiety was given to a large group of individuals and the scores are from a normally distributed population in which the mean is 50 and the SD is 10
1) Approximately what % of individuals earned scores below 50?
2) Approximately what % of individuals earned scores above 60
3) Approximately what % of individuals earned scores below 30?
4) Approximately what % of individuals earned scores between 60 and 70?
5) Approximately what % of individuals earned scores between 30 and 70?
6) A score of 60 on this test would give an individual a percentile rank of?
7) The average cost of a new car today is $17,500. If this is normally distributed with a SD of $2000 compute the following. If I am only willing to pay up to $15,500, what percentage of the total number of cars will fall inside my budget?
Answers
1) 50% 2) 16% 3) 2.15% 4) 13.6% 5) 95.4% 6) 84% 7) 16%